safe adversarial inverse reinforcement learning (S-AIRL)
a safety-aware IRL algorithm with an application of highway driving scenario
Motivation
Reinforcement learning (RL) has achieved lots of success in training the optimal control policies. One step further, given the expert demonstrations, inverse reinforcement learning (IRL) can avoid the necessity of hand-tuning the reward function. However, similar to other policy learning algorithms, IRL suffers from safety concerns. What’s more, IRL is even more vulnerable to unsafety, as it can only infer the importance of safety from the distribution matching. In this project, a safety-aware inverse reinforcement learning algorithm has been developed to improve the safety of the algorithm.
Methodologies
- The overall structure is shown in the following picture. More details can be found in our paper [4].
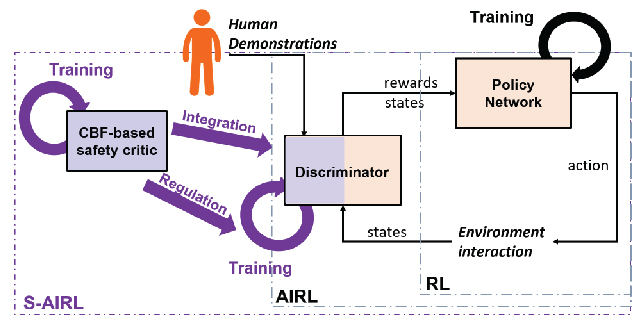
-
First of all, to quantify the safety level of state-action pairs \((s, a)\), a safety critic network is trained based on the guidance of the control barrier function (CBF) technique. The model-based knowledge (CBF) incorporated into the model-free method (safety critic network) can avoid the necessity of training another guiding policy and render a more sufficient exploration. As a result, the trained CBF-based safety critic \(Q^{\textrm{CBF}}_{\textrm{safe}}(s,a)\) can quantify the safety probability of the state-action pairs in the future.
-
Second, to inject the safety awareness, the trained safety critic \(Q^{\textrm{CBF}}_{\textrm{safe}}(s, a)\) is integrated with the discriminator such that the safety feature will be considered in the distribution discrimination process (between trajectories from expert and learned policy).
-
Third, to make sure safety plays an important role, a regulator is added to the algorithm to prevent the recovered reward from assigning high rewards to the risky state-action pairs.
Results
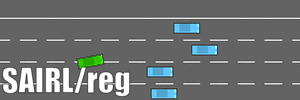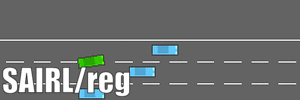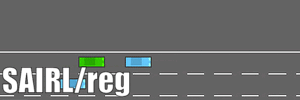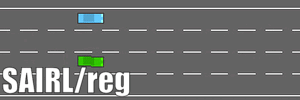
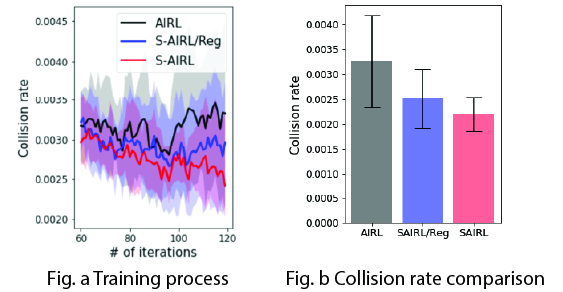
- The training algorithm is written with Tensorflow. We test our algorithm in the highway driving scenario with the simulator highway-env, where the environmental cars are modeled by IDM and MOBIL.

-
Albation test is also conducted without the regulator, i.e., SAIRL/Reg.
-
The scripts run in the high-performance computing (HPC) resources Palmetto cluster at Clemson University. To facilitate the HPC process, parallel samplers are written with Ray to improve the sampling speed greatly. The codes of AIRL and PPO with parallel sampling feature can be found in my Github repository
-
Comparing to the benchmark IRL algorithm AIRL, the collision rate with S-AIRL has been reduced by 30%.
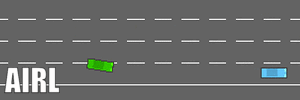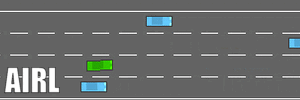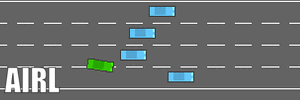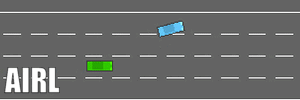
- The driving comparisons (under four parallel driving preceding cars) are shown here.